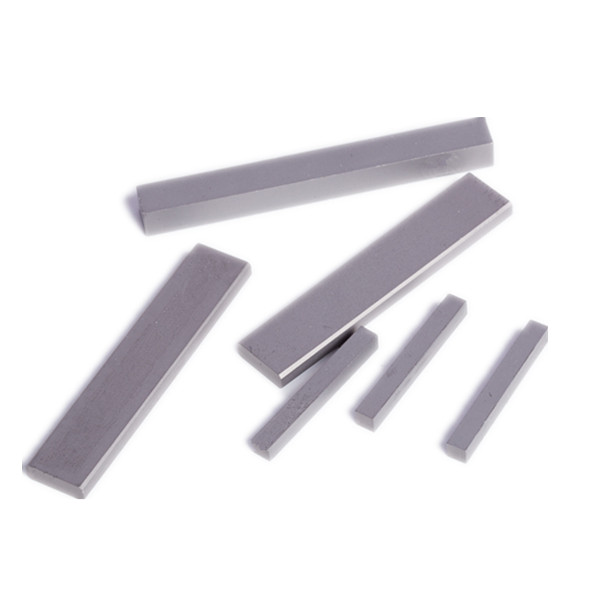
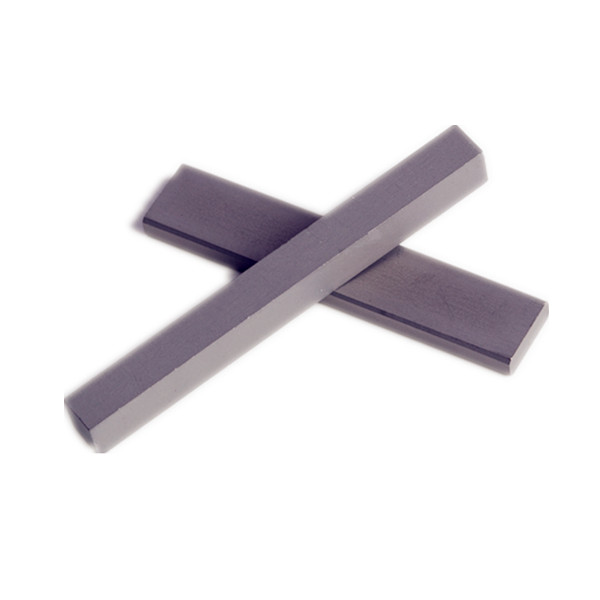
Tungsten carbide plate grades:
| Grade | Composition (%) | Density (g/cm3) | Hardness (HRA) | T.R.S (N/mm²) |
| YG6A | 6%co 94%wc | 14.85 | ≥92.5 | ≥2000 |
| YG8 | 8%co 92%wc | 14.7 | ≥89.8 | ≥2800 |
| YG10X | 10%co 90%wc | 14.35 | ≥91.5 | ≥3600 |
| YG11 | 11%co 89%wc | 14.4 | ≥88.5 | ≥2900 |
| YG15 | 15%co 85%wc | 14 | ≥87.0 | ≥3000 |
| YG20 | 20%co 80%wc | 13.5 | ≥85.5 | ≥2800 |
| YG13X | 13%co 87%wc | 14.2 | ≥90.0 | ≥3200 |
| BT15 | 10%co 90%wc | 14.35 | ≥92.2 | ≥3900 |
| YG6A | Fine grain alloy, good wear resistance. It is suitable for manufacturing forming cutter, wear-resistant parts etc. |
| YG8 | High bending strength, wear resistance lower than YG6A, suitable for manufacturing forming cutter, wear-resistant parts etc. |
| YG11 | |
| YG15 | Suitable for manufacturing punching dies, wear-resistant parts etc. |
| YG20 | High bending strength, suitable for manufacturing progressive dies and other punching dies. |
| YG13X | |
| BT15 | Ultra-fine grain size, High performance, making cutting tools, suitable for cutting ordinary alloy steel, aluminum alloy, heat resistant alloy, cast iron, etc. |
Tungsten carbide plate sizes:
| Length L(mm) |
Width W(mm) |
Thicknes T(mm) |
Length Tolerance(mm) |
Width Toleranee(mm) |
Thickness Tolerance(mm) |
| 330 | 2~3 | 1~3 | +7.0 +3.0 |
+0.4 +0.2 |
+0.35 +0.15 |
| 330 | 3~8 | 1~3 | +7.0 +3.0 |
+0.5 +0.3 |
+0.35 +0.15 |
| 330 | 8~14 | 2~5 | +7.0 +3.0 |
+0.5 +0.3 |
+0.35 +0.15 |
| 330 | 14~34 | 2~11 | +7.0 +3.0 |
+0.6 +0.4 |
+0.5 +0.2 |
Tungsten carbide plate details:
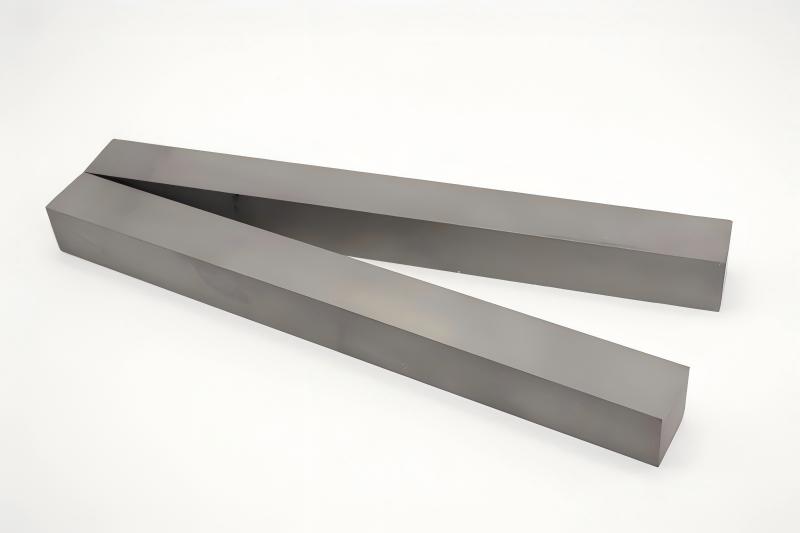
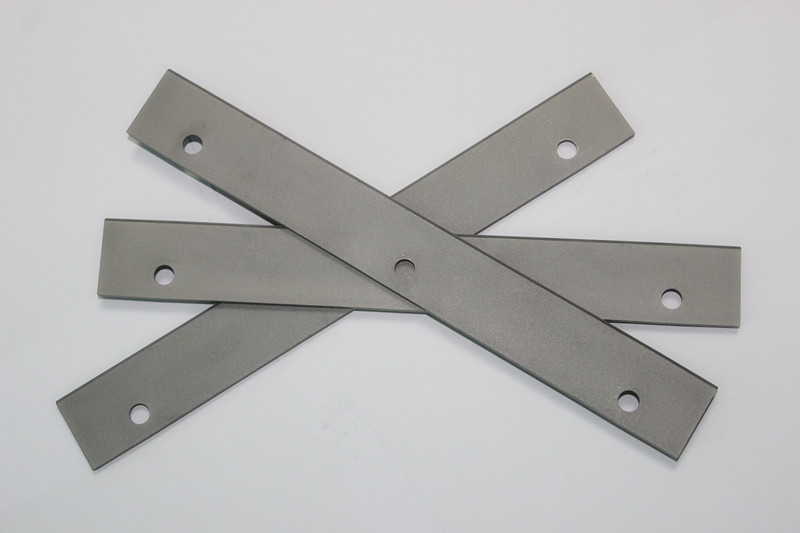


Primary Applications of Tungsten Carbide Plates:
Tungsten carbide plates are widely utilized in industrial sectors requiring exceptional wear resistance, impact resistance, and stability due to their superior properties. Below are their core application scenarios:
1.Wear-Resistant Components and Liner Plates
This is the most classic application. The plates are directly machined into various wear-resistant parts for harsh working conditions.
Typical Applications: Liner plates for mining machinery, pump components handling abrasive slurries, chute liners in cement plants, and scraper blades for conveyor belts.
Function: Protect main equipment structures from wear caused by high-velocity granular materials (e.g., ores, sand, coal powder), significantly extending service life and reducing downtime for replacements.
2.Stamping and Forming Dies
Blanking Dies: Especially for precision and high-wear applications such as silicon steel sheet punching, electronic component lead frame stamping, and ceramic tile extrusion molds. Tungsten carbide dies offer a service life tens to hundreds of times longer than steel dies, ensuring dimensional stability in long-term production.
Drawing Dies: Used for wire and rod drawing, as well as deep drawing of metal cups. Their low friction coefficient and high surface finish minimize product scratches and improve quality.
Cold Heading and Cold Extrusion Dies: Ideal for forming metals at room temperature, where dies endure extreme pressure and friction.
3.Precision Measurement and Positioning Components
Applications: Gauge blocks, calipers, V-blocks, guide rails, and sliding plates.
Reason: Tungsten carbide exhibits exceptional dimensional stability, wear resistance, minimal thermal expansion, and corrosion resistance. This ensures the long-term accuracy of precision measuring tools and prevents wear-induced gaps in positioning components.
4.Tool Substrates and Blades
While most cutting inserts are pre-shaped, plates serve as raw material for manufacturing these blades.
Applications: Plates are processed via wire cutting or grinding to produce blades for lead cutters, PCB V-CUT knives, and specially shaped shear blades. These tools are used for machining solid wood, particleboard, plastics, cast steel, cast iron, forgings, and stainless steel.
Please send us inquiries for quotations and free samples for testing:






